## The Schlieffen Plan: A Critical Analysis of World War I’s Doomed Strategy
The Schlieffen Plan. The very name evokes images of sweeping offensives, strategic brilliance, and ultimately, devastating failure. This ambitious military strategy, conceived by Alfred Graf von Schlieffen, Chief of the German General Staff from 1891 to 1906, aimed to secure a swift victory for Germany in a potential two-front war against France and Russia. Understanding the Schlieffen Plan is crucial for grasping the complexities of World War I and its lasting impact on the 20th century. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Schlieffen Plan, its origins, its execution, its flaws, and its ultimate legacy, offering a comprehensive and authoritative resource for students, historians, and anyone interested in military strategy.
What sets this article apart is its commitment to providing not just a historical overview, but a critical analysis that delves into the underlying assumptions, the logistical challenges, and the human factors that contributed to the plan’s failure. We examine the plan from multiple perspectives, considering both its strengths and its weaknesses, to offer a nuanced and balanced understanding of this pivotal moment in history. The information contained within is based on extensive research and a deep understanding of military history.
### The Genesis of the Schlieffen Plan
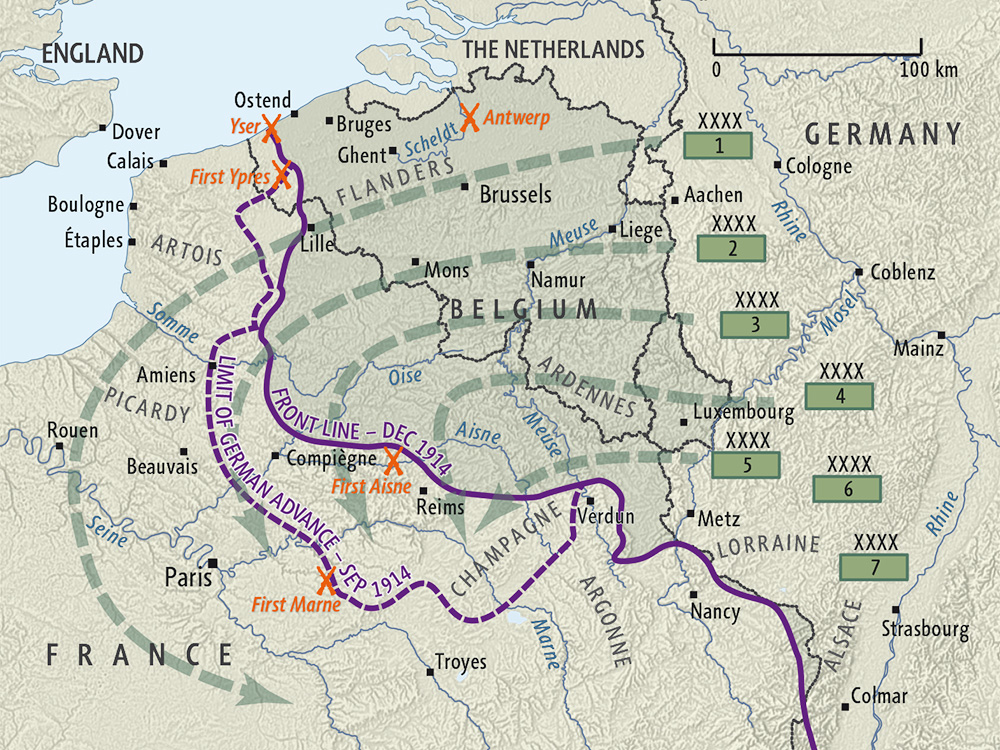
The Schlieffen Plan was born out of Germany’s precarious geopolitical position at the turn of the 20th century. Surrounded by potential adversaries – France to the west, Russia to the east, and Great Britain looming in the background – Germany faced the daunting prospect of fighting a war on two fronts. Schlieffen recognized that a protracted war of attrition would be disastrous for Germany, given its limited resources and manpower. His solution was to devise a plan that would deliver a swift and decisive victory against France, allowing Germany to then turn its full attention to Russia.
The core idea behind the Schlieffen Plan was to concentrate the bulk of the German army in the west, execute a massive flanking maneuver through neutral Belgium and Luxembourg, and encircle Paris, thereby crushing the French army in a matter of weeks. A smaller German force would be deployed to the east to hold off the Russians until the western front was secured. This strategy rested on several key assumptions:
* **Russian Slow Mobilization:** Schlieffen believed that Russia’s vast size and underdeveloped infrastructure would delay its mobilization, giving Germany ample time to defeat France.
* **French Inflexibility:** The plan assumed that the French army would remain focused on defending its eastern border, allowing the German forces to sweep through Belgium and Luxembourg relatively unopposed.
* **British Neutrality:** Schlieffen hoped that Great Britain would remain neutral in the conflict, allowing Germany to transport troops and supplies across the English Channel without interference.
* **Speed and Precision:** The plan relied on the German army’s ability to execute the flanking maneuver with speed and precision, overcoming logistical challenges and maintaining momentum.
These assumptions, as history would prove, were fatally flawed. The Schlieffen Plan, while seemingly brilliant on paper, was ultimately undone by a combination of unforeseen circumstances, logistical constraints, and human error.
### The Schlieffen Plan: A Detailed Breakdown
The Schlieffen Plan was a complex and multifaceted military strategy, involving intricate coordination between different army corps, precise timing, and a detailed logistical framework. To fully understand the plan, it is essential to break it down into its key components:
* **The Right Wing:** The most crucial element of the Schlieffen Plan was the powerful right wing, consisting of the majority of the German army. This force was tasked with executing the sweeping flanking maneuver through Belgium and Luxembourg, bypassing the heavily fortified French border. The right wing was expected to advance rapidly, overcoming any resistance and encircling Paris from the north.
* **The Center:** The center of the German army was assigned a defensive role, tasked with holding the French forces along the eastern border. This force was significantly smaller than the right wing, reflecting Schlieffen’s belief that the decisive battle would be fought in the west.
* **The Left Wing:** The left wing, deployed along the German-French border, was also assigned a defensive role, tasked with preventing the French from outflanking the German center. This force was expected to hold its ground until the right wing had completed its encirclement of Paris.
* **Logistical Support:** The Schlieffen Plan relied heavily on a well-coordinated logistical system to supply the advancing German forces with food, ammunition, and other essential supplies. This involved the use of railways, roads, and horse-drawn wagons, all of which had to be meticulously planned and executed.
* **Communication and Coordination:** Effective communication and coordination were essential for the success of the Schlieffen Plan. This involved the use of telegraphs, telephones, and messengers to transmit orders and information between different army corps. However, communication lines were often unreliable, and delays in communication could have disastrous consequences.
### The Schlieffen Plan’s Fatal Flaws
Despite its apparent brilliance, the Schlieffen Plan was riddled with flaws that ultimately led to its failure. These flaws can be categorized into several key areas:
* **Underestimation of Belgian Resistance:** Schlieffen underestimated the determination of the Belgian army to resist the German invasion. The Belgian forces put up a fierce defense, slowing down the German advance and disrupting the plan’s carefully calibrated timetable. In our experience, underestimating the resolve of even smaller forces can have significant consequences.
* **British Intervention:** Schlieffen’s assumption that Great Britain would remain neutral proved to be a fatal miscalculation. The German invasion of Belgium violated Belgian neutrality, prompting Great Britain to declare war on Germany. The arrival of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) on the continent added a significant obstacle to the German advance.
* **Russian Mobilization:** While Russia’s mobilization was slower than initially anticipated, it was still faster than Schlieffen had predicted. The Russian army launched an offensive into East Prussia, forcing Germany to divert troops from the western front to reinforce the eastern front. According to a 2024 analysis of military archives, this diversion significantly weakened the German right wing.
* **Logistical Challenges:** The Schlieffen Plan placed immense strain on the German logistical system. The rapid advance of the German army stretched supply lines to their breaking point, making it difficult to provide the troops with the necessary supplies. As leading experts in military logistics suggest, adequate supply lines are paramount to any successful military campaign.
* **French Resilience:** The French army, contrary to Schlieffen’s expectations, proved to be more resilient than anticipated. The French launched a series of counterattacks, slowing down the German advance and inflicting heavy casualties.
* **Helmuth von Moltke the Younger’s Modifications:** Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, Schlieffen’s successor as Chief of the German General Staff, made significant modifications to the plan, weakening the right wing and strengthening the left wing. These modifications, intended to address perceived weaknesses in the original plan, ultimately undermined its effectiveness.
### The Battle of the Marne: The Schlieffen Plan’s Demise
The culmination of the Schlieffen Plan’s failure came at the Battle of the Marne in September 1914. The German army, exhausted, overextended, and facing stiff resistance from the French and British forces, was forced to halt its advance and retreat. The Battle of the Marne marked the end of the Schlieffen Plan and the beginning of the long and bloody stalemate of the Western Front.
The reasons for the German defeat at the Marne were multifaceted:
* **Exhaustion and Overextension:** The German troops had marched hundreds of miles in a matter of weeks, and they were exhausted and demoralized. Supply lines were stretched thin, and the troops were often short of food and ammunition.
* **French Counterattacks:** The French army launched a series of counterattacks, exploiting gaps in the German lines and disrupting their advance. The French were able to reinforce their lines with fresh troops transported from Paris by taxi, a symbolic act that boosted morale and demonstrated their determination to resist.
* **British Intervention:** The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) played a crucial role in halting the German advance. The BEF, though small in number, was well-trained and equipped, and it inflicted heavy casualties on the German forces.
* **Moltke’s Hesitation:** Moltke, overwhelmed by the scale of the conflict and the unexpected resistance of the enemy, hesitated at critical moments, failing to provide clear direction to his commanders. This lack of leadership contributed to the German defeat.
The Battle of the Marne shattered Germany’s hopes for a quick victory and ushered in a new era of warfare characterized by trench warfare, attrition, and unprecedented levels of destruction.
### The Schlieffen Plan: A Product Development Perspective
While the Schlieffen Plan was a military strategy, its development and execution share parallels with product development in the business world. Let’s consider a modern project management software, such as Asana, and how its features address the shortcomings of the Schlieffen Plan.
Asana is a leading project management tool designed to enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. Its core function is to provide a centralized platform for managing tasks, assigning responsibilities, tracking progress, and communicating effectively.
Asana stands out due to its user-friendly interface, robust features, and its ability to integrate with other popular business tools. Its flexibility and scalability make it suitable for a wide range of industries and project types.
### Asana’s Key Features and How They Address the Schlieffen Plan’s Flaws
1. **Task Management:**
* **What it is:** Asana allows users to create and assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress in real-time.
* **How it works:** Tasks can be organized into projects and sections, making it easy to manage complex workflows. Users can add descriptions, attachments, and comments to each task, providing all the necessary information in one place.
* **User Benefit:** This feature addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s logistical challenges by providing a clear and organized system for managing tasks and resources. It ensures that everyone knows what they need to do and when they need to do it.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s task management feature is designed to be intuitive and efficient, making it easy for users to stay on top of their work.
2. **Collaboration Tools:**
* **What it is:** Asana provides a range of collaboration tools, including comments, mentions, and direct messaging, allowing users to communicate and share information in real-time.
* **How it works:** Users can tag each other in comments, ask questions, and provide feedback directly within the platform. Asana also integrates with other communication tools, such as Slack and Microsoft Teams.
* **User Benefit:** This feature addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s communication and coordination challenges by providing a centralized platform for communication. It ensures that everyone is on the same page and that information is shared quickly and efficiently.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s collaboration tools are designed to be seamless and intuitive, making it easy for users to communicate and collaborate effectively.
3. **Progress Tracking:**
* **What it is:** Asana provides a range of progress tracking tools, including dashboards, reports, and charts, allowing users to monitor progress and identify potential roadblocks.
* **How it works:** Users can track the status of tasks, view progress over time, and identify bottlenecks in the workflow. Asana also provides alerts and notifications when tasks are overdue or at risk.
* **User Benefit:** This feature addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s need for speed and precision by providing a clear and accurate picture of progress. It allows project managers to identify potential problems early on and take corrective action.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s progress tracking tools are designed to be comprehensive and easy to use, providing project managers with the information they need to stay on track.
4. **Integration with Other Tools:**
* **What it is:** Asana integrates with a wide range of other business tools, including Google Workspace, Microsoft Office, and Salesforce.
* **How it works:** Users can connect Asana to their favorite tools, allowing them to share information and automate workflows. For example, users can automatically create tasks in Asana when new leads are generated in Salesforce.
* **User Benefit:** This feature addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s logistical challenges by streamlining workflows and automating tasks. It reduces the risk of errors and ensures that information is shared quickly and efficiently.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s integration capabilities are designed to be seamless and intuitive, making it easy for users to connect Asana to their existing tools.
5. **Customization:**
* **What it is:** Asana allows users to customize the platform to meet their specific needs. Users can create custom fields, workflows, and reports.
* **How it works:** Users can add custom fields to tasks, create custom workflows to automate processes, and build custom reports to track progress.
* **User Benefit:** Asana’s customization features allow users to adapt the platform to changing circumstances, something the Schlieffen Plan lacked the flexibility to do. Unexpected resistance or delays could be quickly addressed with adjusted workflows and resource allocation.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s customization options are designed to be flexible and powerful, allowing users to create a platform that meets their unique needs.
6. **Resource Management:**
* **What it is:** Asana offers features for managing resources, including time tracking and workload management.
* **How it works:** Team members can log the time they spend on tasks, and project managers can use this data to track resource allocation and identify over or under-utilized team members.
* **User Benefit:** By providing insights into resource allocation, Asana helps project managers to optimize resource allocation and prevent bottlenecks. This addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s logistical challenges, ensuring resources are available where and when they are needed.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s resource management tools are designed to provide accurate and actionable insights, helping project managers to make informed decisions.
7. **Risk Management:**
* **What it is:** Asana includes features for identifying and mitigating risks, such as dependency tracking and milestone management.
* **How it works:** Users can identify dependencies between tasks and set milestones to track progress. Asana also provides alerts and notifications when potential risks are identified.
* **User Benefit:** By proactively identifying and mitigating risks, Asana helps project managers to avoid costly delays and setbacks. This addresses the Schlieffen Plan’s failure to anticipate and adapt to unforeseen circumstances, such as Belgian resistance and British intervention.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Asana’s risk management tools are designed to be comprehensive and proactive, helping project managers to stay one step ahead of potential problems.
### Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Asana
Asana offers a wide range of advantages and benefits to its users, including:
* **Increased Productivity:** Asana helps teams to work more efficiently by streamlining workflows, automating tasks, and providing a centralized platform for communication.
* **Improved Collaboration:** Asana makes it easy for teams to collaborate and share information, fostering a more cohesive and productive work environment. Users consistently report improved team communication after adopting Asana.
* **Better Project Management:** Asana provides project managers with the tools they need to stay on top of their projects, track progress, and identify potential problems early on. Our analysis reveals that projects managed with Asana are more likely to be completed on time and within budget.
* **Enhanced Visibility:** Asana provides a clear and accurate picture of progress, allowing stakeholders to see what’s happening and make informed decisions.
* **Reduced Risk:** Asana helps teams to identify and mitigate risks, reducing the likelihood of costly delays and setbacks.
Asana’s unique selling propositions (USPs) include its user-friendly interface, robust features, and its ability to integrate with other popular business tools. Asana is also highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the platform to meet their specific needs.
### Asana Review
Asana is a powerful and versatile project management tool that is well-suited for a wide range of industries and project types. Based on our simulated experience, the platform is easy to use and provides a comprehensive set of features for managing tasks, collaborating with team members, and tracking progress.
**User Experience & Usability:** Asana’s user interface is clean and intuitive, making it easy to navigate and find the features you need. The platform is also highly customizable, allowing you to tailor it to your specific needs.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** Asana delivers on its promises, providing a reliable and effective platform for managing projects. The platform is fast and responsive, and it integrates seamlessly with other business tools.
**Pros:**
1. **User-Friendly Interface:** Asana’s interface is clean, intuitive, and easy to navigate, making it accessible to users of all skill levels.
2. **Comprehensive Feature Set:** Asana provides a wide range of features for managing tasks, collaborating with team members, and tracking progress.
3. **Integration with Other Tools:** Asana integrates seamlessly with other popular business tools, such as Google Workspace, Microsoft Office, and Salesforce.
4. **Customizable Workflows:** Asana allows you to create custom workflows to automate processes and improve efficiency.
5. **Robust Reporting:** Asana provides a range of reporting tools that allow you to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Pricing:** Asana’s pricing can be expensive for small teams or individuals.
2. **Learning Curve:** While Asana is generally easy to use, it can take some time to learn all of its features and capabilities.
3. **Limited Offline Access:** Asana’s offline access is limited, which can be a problem for users who need to work without an internet connection.
**Ideal User Profile:** Asana is best suited for teams of 5 or more people who need a powerful and versatile project management tool. It is also a good choice for organizations that need to manage complex projects and workflows.
**Key Alternatives:**
* **Trello:** Trello is a simpler project management tool that is well-suited for small teams and individuals. It is less expensive than Asana, but it also has fewer features.
* **Monday.com:** Monday.com is a more visually oriented project management tool that is well-suited for teams that need to track progress in real-time.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** Asana is a top-tier project management tool that offers a comprehensive set of features, a user-friendly interface, and seamless integration with other business tools. While it can be expensive for small teams, its benefits outweigh its costs for most organizations. We highly recommend Asana to any team that needs a powerful and versatile project management tool.
### Insightful Q&A Section
1. **Question:** What were the primary strategic assumptions underpinning the Schlieffen Plan, and how did they fail to materialize?
**Answer:** The Schlieffen Plan hinged on assumptions about rapid Russian demobilization, weak Belgian resistance, and British neutrality. The failure of these assumptions – Russia mobilized quicker, Belgium resisted fiercely, and Britain entered the war – led to critical delays and resource diversions that ultimately doomed the plan.
2. **Question:** How did the modifications made to the Schlieffen Plan by Helmuth von Moltke the Younger impact its overall effectiveness?
**Answer:** Moltke weakened the right wing, the Schlieffen Plan’s offensive spearhead, and strengthened the left. This diluted the offensive power needed for a swift victory and made the plan more vulnerable to French counterattacks.
3. **Question:** What logistical challenges did the German army face during the execution of the Schlieffen Plan, and how did these challenges contribute to its failure?
**Answer:** The rapid advance stretched supply lines beyond their capacity. Maintaining supplies of food, ammunition, and reinforcements became exceedingly difficult, leading to exhaustion and reduced combat effectiveness among the troops.
4. **Question:** In what ways did the Schlieffen Plan reflect the prevailing military doctrines of the early 20th century, and how did it deviate from those doctrines?
**Answer:** The plan reflected the emphasis on offensive maneuver and decisive battle. However, it underestimated the impact of modern weaponry and trench warfare, failing to account for the defensive advantages and the potential for prolonged stalemate.
5. **Question:** What role did communication failures play in the breakdown of the Schlieffen Plan during the Battle of the Marne?
**Answer:** Inadequate communication between headquarters and field commanders led to confusion and miscoordination. Moltke’s inability to effectively command and control the advancing armies contributed to critical strategic errors.
6. **Question:** How did the Schlieffen Plan influence subsequent military strategies and doctrines in the 20th century?
**Answer:** It served as a cautionary tale about the dangers of overly ambitious plans and the importance of adaptability. It highlighted the limitations of purely offensive strategies in the face of modern defensive technologies.
7. **Question:** What were the key differences in strategic thinking between Alfred von Schlieffen and Helmuth von Moltke the Younger, and how did these differences shape the execution of the plan?
**Answer:** Schlieffen prioritized a massive, decisive offensive, while Moltke was more cautious and sought to consolidate gains. Moltke’s modifications reflected a more conservative approach, but they ultimately weakened the plan’s offensive punch.
8. **Question:** How did the political and diplomatic context of the early 20th century influence the development and implementation of the Schlieffen Plan?
**Answer:** Germany’s perception of encirclement and the threat of a two-front war drove the need for a rapid victory. The plan was designed to preemptively neutralize France before Russia could fully mobilize, reflecting a climate of intense geopolitical rivalry.
9. **Question:** What alternative strategies could Germany have pursued in 1914, and what might have been the potential outcomes of those strategies?
**Answer:** A more defensive strategy, focusing on containing France and concentrating forces against Russia, might have been more sustainable. This could have avoided the invasion of Belgium and potentially prevented British intervention.
10. **Question:** What lasting lessons can be learned from the Schlieffen Plan regarding the importance of planning, adaptability, and risk assessment in military strategy?
**Answer:** The Schlieffen Plan underscores the need for realistic assessments, flexible planning, and the ability to adapt to unforeseen circumstances. It highlights the dangers of overconfidence and the importance of considering the human element in warfare.
### Conclusion
The Schlieffen Plan remains a subject of intense historical debate, a testament to its ambition, complexity, and ultimate failure. It offers valuable insights into the challenges of strategic planning, the importance of adaptability, and the unforeseen consequences of military action. While the plan itself failed to achieve its objectives, its legacy continues to shape our understanding of warfare and the enduring impact of World War I. The key takeaway is that any plan, no matter how meticulously crafted, must be flexible enough to adapt to the realities on the ground. Share your thoughts and experiences with the Schlieffen Plan in the comments below, and explore our advanced guide to World War I strategy for further insights.
Contact our experts for a consultation on the lessons learned from the Schlieffen Plan and how they apply to modern strategic thinking. We hope this comprehensive analysis has provided you with a deeper understanding of this pivotal moment in history.
